We can start by enumerating what are the main vectors that attackers use to get into victims: phishing, brute forcing and the use of exploits. Let's use this information to understand what exactly are attackers doing from a technical point of view, but more importantly, to monitor how their campaigns evolve. And here we want to highlight the importance of continuously tracking malicious activity in order to feed our systems accordingly: attackers evolve their methods and the IOCs used constantly change. We need the whole movie, not just a static picture.
This post describes different examples of techniques we can use to monitor ransomware campaigns, with a special focus on the infection vectors previously mentioned in order to minimize the risk of becoming a victim.
For more details, you can check our recorded anti-ransomware webinar in English and Spanish.
Ransomware in phishing attacks
Phishing is the most common technique used to distribute ransomware. We want to be able to discover how it is being used in new ransomware campaigns and to obtain the infrastructure behind the attack, gathering valuable IOCs and TTPs to feed our defenses.We can start looking for emails involved in phishing campaigns uploaded this year to VirusTotal:
engines:ransom type:email fs:2020-01-01+
We get a list of generic ransomware email files. We can specify a certain malware family we are interested in. For instance, the following query returns emails related to some of the most common campaigns:
(engines:bitpaymer OR engines:maze OR engines:Ryuk OR engines:gandcrab OR engines:clop OR engines:revil OR engines:sodibiniki OR engines:matrix) type:email
Expanding different nodes uncovers new IOCs to feed our defenses and unfolds this campaign, showing domain names that were used to bait victims into opening the malicious word document attached to the phishing email.
This kind of phishing attacks where legitimate logos, domains and brand images are used to bait victims into executing malware can hurt a company's reputation, not to speak of being used against the company itself. The sooner we detect a campaign the faster we can perform actions to shut it down. VirusTotal’s Livehunt checks any submitted file against a search criteria written in Yara.
For example, to check for embedded domains in emails detected as phishing, we could use:
According to this report, the four CVEs that are most frequently used for performing ransomware attacks this year are:
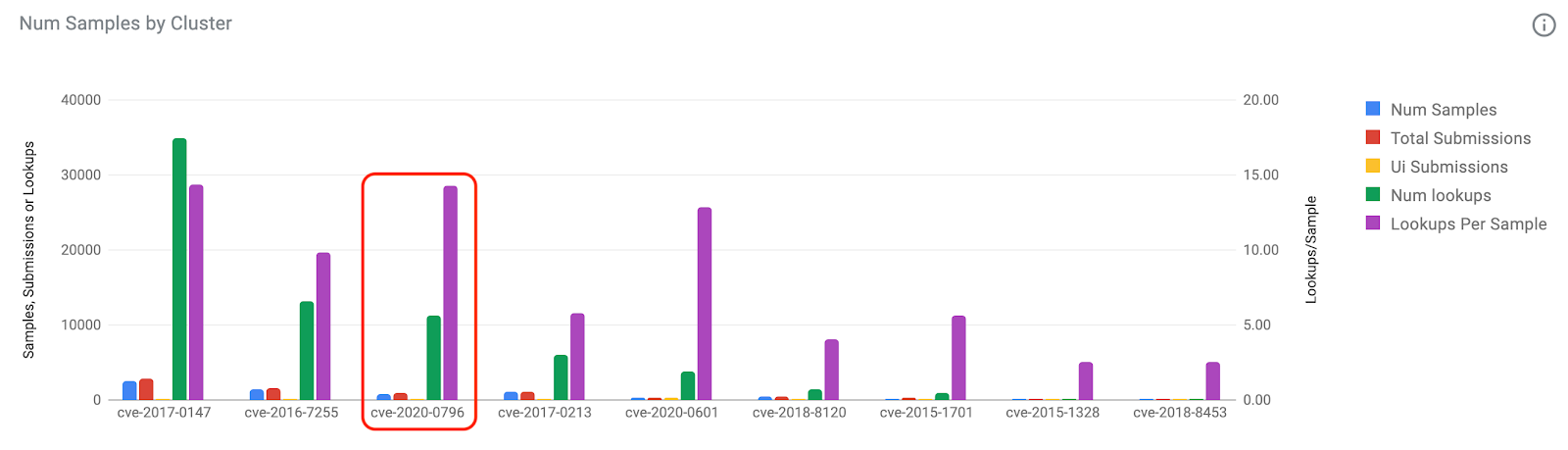
We could use the following query to get more detailed information about what CVEs were used in ransomware attacks during 2020:
For example, to check for embedded domains in emails detected as phishing, we could use:
import "vt"
rule brandmon_google {
strings:
$domain1 = "accounts.google.com"
$domain2 = "mail.google.com"
$domain6 = "drive.google.com"
condition:
for any engine, signature in vt.metadata.signatures : (
signature contains "phishing" and vt.metadata.file_type == vt.FileType.EMAIL and (any of them)
)
}Exploits used in ransomware attacks
Exploits are commonly used for installing malware or for escalating privileges into your system.According to this report, the four CVEs that are most frequently used for performing ransomware attacks this year are:
- CVE-2019-19781 → Revil/Sodinokibi, Ragnarok, DopplePaymer, Maze, CLOP y Nephilim.
- CVE-2019-11510 → Revil/Sodinokibi y Black Kingdom
- CVE-2012-0158 → EDA2 y RASOM
- CVE-2018-8453 → Revil/Sodinokibi
We could use the following query to get more detailed information about what CVEs were used in ransomware attacks during 2020:
engines:ransom tag:exploit fs:2020-01-01+ tag:CVE-2020*
Now, we are ready to create a Livehunt rule to find new files tagged with one of the exploits frequently used by ransomware.
import "vt"
rule ransomware_exploits {
condition:
for any tag in vt.metadata.tags : (
tag == "cve-2019-19781" or
tag == "cve-2019-11510" or
tag == "cve-2012-0158" or
tag == "cve-2018-8453" or
tag == "cve-2020-1472" or
tag == "cve-2020-0796"
) and not vt.metadata.file_type == vt.FileType.CAP
}This will result in an immediate notification, allowing us tracking any new IOCs we can use to protect our system.
More importantly, this is very valuable information we can use on a regular basis to manage our patching policy, prioritizing patches based on fresh data of how different exploits are being used in real attacks.
As an example, we can start with a recent DFIR Report investigation revealing Ryuk exploiting zerologon. There are many ways to track campaigns, however VT Graph is a great choice to get together all the discovered observables and extend our knowledge in a visual way. Here are some tips that could help you during this process:
More importantly, this is very valuable information we can use on a regular basis to manage our patching policy, prioritizing patches based on fresh data of how different exploits are being used in real attacks.
Tracking fresh campaigns
Now, we want to make sure that we monitor any new ransomware campaign in order to understand how it evolves and what new artefacts and techniques they use.As an example, we can start with a recent DFIR Report investigation revealing Ryuk exploiting zerologon. There are many ways to track campaigns, however VT Graph is a great choice to get together all the discovered observables and extend our knowledge in a visual way. Here are some tips that could help you during this process:
- Start by adding all the known observables to a new VT Graph.
- Expand domains, URLs and IPs to unfold relations and obtain new observables.
- In order to keep our list of observables up to date, we can translate common Yara rules into Livehunt rules to catch new files, injecting Livehunts results directly into the graph.
- Additionally, we can use Retrohunt rules to look for similar samples in our collection.
We start the investigation dropping one of the files included in the publication in a new graph, showing domains, urls and ip addresses embedded in the file, ITW URLs hosting the file and network observables contacted by this sample when executed. This file is detected as “bazar” malware, used to install Ryuk. We dropped all this information in our graph:

Additionally to keep pivoting using our graph and indicators, we can also translate the Yara rules from the DFIR report into Livehunt rules.

We can integrate Livehunt results into our graph in just two clicks. Just click on the target icon at the right in the VTGrap interface, select the rule desired and choose "Load results". This will add all the new observables that match our rules to the current graph. We can expand these new nodes to unveil new observables and create relationships.

All these new IOCs are fresh observables that are clearly related to this campaign. All this continuous flow of fresh indicators will help us improve our security mechanisms to stop Ryuk from passing through our defenses.
Summarizing, the knowledge of what attackers are using is the first necessary step for us to minimize our exposure to different campaigns. It wouldn't be right to put all the different ransomware attacks under the same umbrella, as they became highly specialized and protecting from different actors is not exactly the same. The techniques described in this post are a good starting point for automatically minimizing our exposure to more spread ransomware campaigns, however they can be applied both for generic and targeted attacks.
Stay safe and happy hunting!
Additionally to keep pivoting using our graph and indicators, we can also translate the Yara rules from the DFIR report into Livehunt rules.
We can integrate Livehunt results into our graph in just two clicks. Just click on the target icon at the right in the VTGrap interface, select the rule desired and choose "Load results". This will add all the new observables that match our rules to the current graph. We can expand these new nodes to unveil new observables and create relationships.

All these new IOCs are fresh observables that are clearly related to this campaign. All this continuous flow of fresh indicators will help us improve our security mechanisms to stop Ryuk from passing through our defenses.
Summarizing, the knowledge of what attackers are using is the first necessary step for us to minimize our exposure to different campaigns. It wouldn't be right to put all the different ransomware attacks under the same umbrella, as they became highly specialized and protecting from different actors is not exactly the same. The techniques described in this post are a good starting point for automatically minimizing our exposure to more spread ransomware campaigns, however they can be applied both for generic and targeted attacks.
Stay safe and happy hunting!
This post was co-authored by Vicente Diaz.


0 comments:
Post a Comment